
Functional Testing: Meet Business Requirements!
Quality Assurance Specialists or Analysts test a web project against a predetermined set of business requirements. To do this, Quality Assurance or QA Functional Testing will assess a website or web application’s functionality and usability.
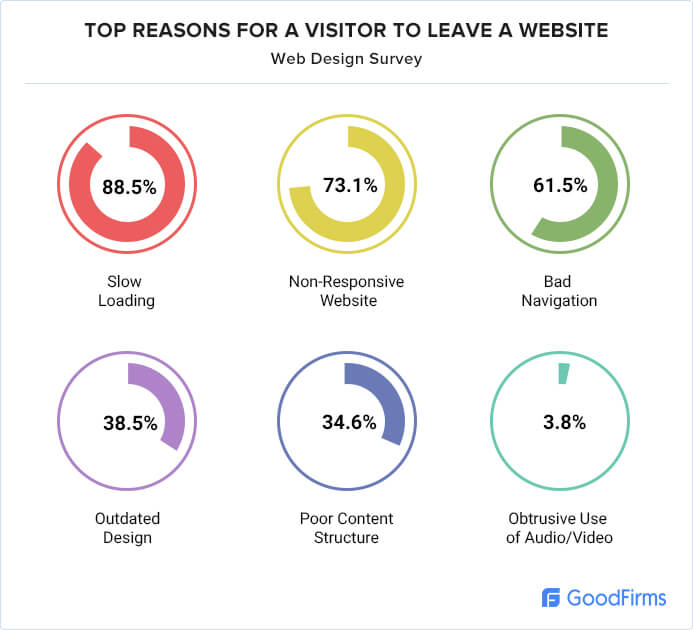
A dedicated website lets Internet users find your pages, services, or products. In addition, people can get in touch with your brand via your site. After all, 38.5% of Internet users will judge a business on the first impressions of their site.
Therefore, Functionality Testing is a significant part of QA efforts to remedy any issues with your web project. The tests aim to uncover functionality bugs in the site or app before it launches or goes live. In addition to saving time, QA Testing can check on the web project’s compatibility and security!
Functional Testing and Its Importance
During Functional Testing, Quality Assurance Experts thoroughly examine a website or web application. They perform tests and check for usability concerns to verify if the project works as intended. The QA team should be able to deliver a product that satisfies both the business and the end users.
As a result, QA Testing is necessary for refining Websites and Web Applications. There is no shortage of bugs and errors in any project. This is why it’s vital to find and fix those bugs during the early stages of web development and testing. Even one design flaw can result in higher Bounce Rates and lower conversions or sales.
Source: GoodFirms.
Comprehensive Website and Web Application QA Testing can eliminate design or function flaws before launch. So, with the help of Functional Testing in your QA Processes, you can accomplish the following:
- Enhanced User Experience;
- Boosted customer retention;
- Reduced website downtime; and
- Upgraded brand reputation.
Types of Functional Testing
A QA Team can ensure that features work as intended through Website and Web Application Functional Testing. As a result, they can provide a web project that only adds to the overall User Experience.
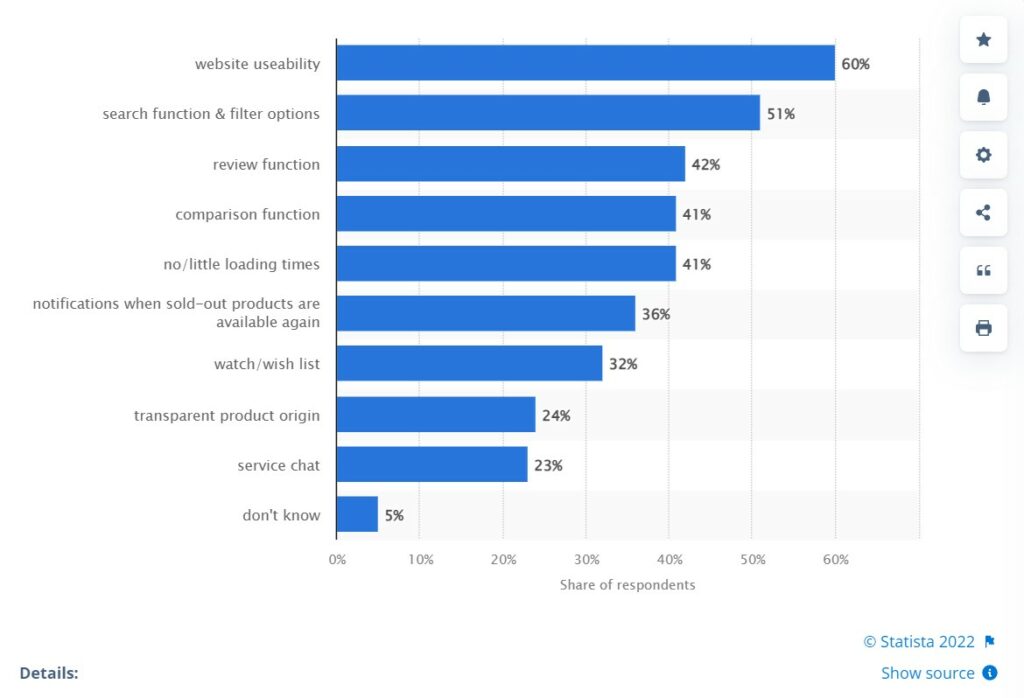
For instance, for eCommerce Websites, a key concern of consumers is website usability. Not only that, but the site will need a product-centered design and online payment capabilities. Also, the site or app should be able to handle multiple users placing their respective product orders simultaneously.
Source: Statista.
There are many types of QA Functional Testing. Some examine the project’s parts or in its entirety. So, here are the most common testing types:
Unit Testing.
Quality Assurance Analysts and Testers examine individual parts or units of a website work by themselves in a White-box format.
Component Testing.
Component or Module Testing will check on the site or app’s parts but in a Black Box format instead.
Smoke Testing.
It will initially examine if a new website or application and its most critical functions meet its objective(s). Another name for this testing type is Build Verification Testing.
Sanity Testing.
This test type focuses on parts of the code that have recently been fixed or have new functionality.
Regression Testing.
This testing type will check if the web project is functioning as intended, especially after changes were made.
Integration Testing.
Integration Testing examines whether individual components or code modules operate correctly in a group.
API Testing.
This test type will check if Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), which interconnect apps or systems, are working properly.
UI Testing.
During User Interface or UI Testing, Quality Assurance Analysts interact with the site or app to examine the User Experience.
System Testing.
QA Professionals will evaluate the entire site or app to see if it meets business requirements. This testing type is also known as End-To-End Testing.
White-box Testing.
This type of test incorporates many of the testing types listed here. But most importantly, it tests a system with a visible internal code, design, and paths.
Black-box Testing.
Unlike the previous type, during Black-box Testing, the system’s code, infrastructure, and other related aspects aren’t visible.
Acceptance Testing.
Quality Assurance Specialists will analyze the web project to ensure that users can achieve the goals set in the requirements document.
Alpha Testing.
During these tests, an internal team will evaluate the web project. These testers will have the most knowledge of the site or app but have no hand in creating it.
Beta Testing.
In Beta Testing, a group of actual end users will test the project. They can give you customer feedback before the launch stage.
Production Testing.
Lastly, Production Testing occurs after the project’s launch. But, QA Testers get more reports on bugs and errors from live users to ensure the site or app’s stability.
Business Requirements and Functionality Testing
Business requirements are critical to any effective Quality Assurance Testing process. These requirements are the objectives of the website or app, which generally include the problems the project will solve. Clients provide these requirements or specifications before the start of the Web Development process.
Fortunately, Quality Assurance efforts can help businesses build web projects that meet business requirements and objectives. QA Functional Testing will test a web project and judge whether the functionality aligns with the requirements. Not only that, but it ensures that the entire project is free of bugs or errors.
Here’s a step-by-step process for identifying website or application business requirements:
- Pinpoint the stakeholders, including clients or end users.
- Next, determine your users, their interests, and concerns.
- Collect more information on users through an empathy map.
- Set up a user flow diagram to learn more about the project’s customer experience.
- Build simple prototypes to learn more about functional requirements.
- Create a user story map to better understand the project backlogs.
Key Techniques for Functional Testing
88% of consumers are “less likely to return” to a website after having a bad UX. For any Quality Assurance team looking to test their web project’s functionality, you must utilize the following testing techniques:
White-box Testing
In White-box Testing, Quality Assurance Analysts are fully aware of the website or application’s internal structure during testing. The system’s structure is clear to the Quality Assurance Specialists, who know or can access the source code.
Thus, Quality Assurance Analysts can more easily point out vulnerabilities, broken elements, and other issues. So, they’ll design test cases more thoroughly in the future. Not only that, but testers can ensure that the internal operations of all project components follow the appropriate frameworks.
Black-box Testing
The first technique for QA Functional Testing is Black-box Testing. Here, the Quality Assurance Tester doesn’t know about the web project’s inner workings. The website or app’s internal structure, architecture, and code are hidden or unknown.
For these tests, the QA Specialists must act like an end-user who doesn’t know the system’s structure! So, the tester can only know the visible project’s external functionality.
As a result, they can easily examine several user-facing aspects of the site or app, including:
- User Interface and User Experience;
- User action responses;
- Response time;
- The web or app server;
- Database;
- Dependencies;
- Integrated systems;
- Usability; and
- Reliability.
Black-box Testing is often combined with White-box Testing efforts. Doing so will achieve a more comprehensive project examination and improve coverage of quality concerns.
Gray-box Testing
In Gray-box Testing, you can test the website or application with some knowledge of its internal workings. This semi-transparent testing method allows a Quality Assurance Specialist to partially understand the site or app’s internal structure.
In Gray-Box Testing, you can test both the project’s user-facing part and its code. This testing technique will examine context-specific concerns and bugs to create a high-quality website or app. It can find defects resulting from improper coding or application use.
Exploratory Testing
The main principle of Exploratory Testing is improvement in your test cases and design. Exploratory Testing is an approach that combines testing experiences and past results to improve future tests on the go. This testing technique is rigorous and structured and will investigate the web project at a high level.
This testing method requires less preparation but can still allow QA Specialists to find significant errors quickly. Thus, Exploratory Testing is generally adopted when the QA Testing team is on a time crunch.
Final Thoughts
A regular business website must ensure its design is inviting and intuitive. Thus, visitors will want to browse their pages for as long as possible. However, the website must function smoothly to ensure that it can effectively attract and convert visitors.
As a result, it’s vital to ensure your website meets business requirements with the help of Quality Assurance Website Testing. Website and Web Application Functional Testing ensures that the QA team will weed out bugs, defects, and other errors.
By following the requirements, Quality Assurance Specialists can deliver a web project that satisfies both the business and the end user.
A dedicated website significantly benefits your brand for various reasons, including engagement. With the right Web QA Tester on your team, your website or app will have higher Conversion Rates.


















Comment 0